توضیحات
Bacteria that use organic matter as a source of energy and carbon are called heterotrophic bacteria. Heterotrophic aerobic bacteria are a diverse group of heterotrophic bacteria that can grow in oxygen-containing environments. Bacteria can be obligate aerobes or facultative anaerobes. Heterotrophic aerobic bacteria play an important role in biological decomposition and their presence in oxygen-rich waters has a vital impact on the efficiency of structures and engineering operations in various industries. Therefore, the MicrobCheckTM AERO kit has been designed and developed for the identification and estimation of the population of this group of bacteria.
If the test is positive for these microorganisms, further tests are needed to identify the type of bacteria present in the sample more accurately, including the production or non-production of acid by these bacteria.
results interpretation
results interpretation
Microorganisms present at the bottom (depth) of the Falcon tube experience oxygen deficiency and seek a substitute for it. A green-blue substance in the medium inside the Falcon serves as a replacement for oxygen. As bacteria consume this substance, its green-blue color gradually fades to yellow or colorless. This process usually starts from the bottom of the Falcon and moves upwards, or it may start from the top and move downwards. The disappearance of the blue color indicates a positive reaction, meaning the creation of viable conditions due to the presence of heterotrophic aerobic bacteria.
Interpretation of observable patterns in the results:
- Yellowing of the medium inside the Falcon from the bottom to the top: In this case, the presence of heterotrophic aerobic bacteria, preferably from the bottom upwards (with initial oxygen), is evident by the yellowing of the medium inside the Falcon, gradually moving towards the top. This situation is usually caused by the presence of obligate aerobic bacteria.
- Yellowing of the environment inside the falcon from the top of the falcon to the bottom: In this condition, the presence of aerobic heterotrophic bacteria is preferably from the surface of the falcon (aerobic) to the bottom (anaerobic), which starts from the surrounding parts of the surface and gradually advances towards the bottom of the falcon, resulting in the yellowing of the environment inside the falcon. This condition is usually caused by the presence of facultative anaerobic bacteria.
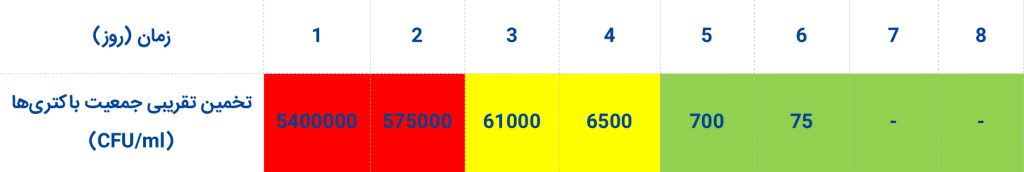
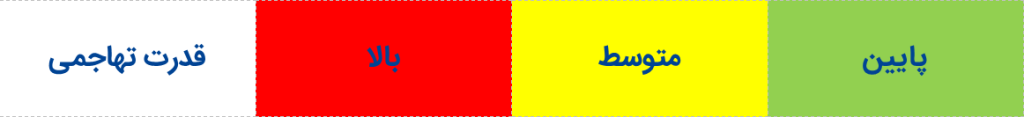
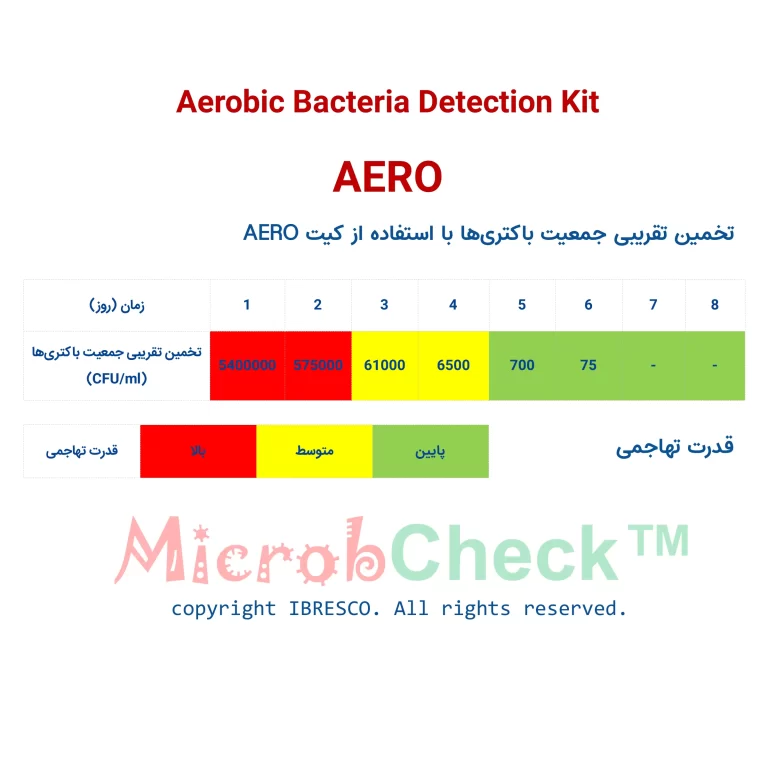
Estimating the approximate population and aggressive potential of bacteria:
If the test result is positive, you can estimate the population and invasion level of the bacteria according to the following tables. A faster response occurs when the population of bacteria is higher.
Observing a positive response on the first day indicates that the bacteria are highly invasive, and in this case, the operation to combat the bacteria should be done as quickly as possible.
Observing a positive response on the second day indicates that the bacteria are invasive, and the fight against them should be considered in the near future.
If a positive reaction is observed on the third day, there is no urgent need to take action to eliminate the bacteria, but the bacterial population should be under routine control by testing with this kit.
A positive reaction on the fourth day indicates the presence of background bacteria in the sample at a normal level. This condition is not of significant importance for follow-up, but appropriate controls should be taken into account.